- Home
- :
- All Communities
- :
- Industries
- :
- Education
- :
- Education Blog
- :
- Using the Data Interoperability Extension to impor...
Using the Data Interoperability Extension to import SDTS DLG files into ArcGIS Pro
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
One of the challenges to working effectively in GIS has been the difficulty of importing certain spatial data formats into a GIS. To meet this challenge, Esri's Data Interoperability Extension has been a longstanding and useful set of tools that enables a wide variety of spatial data formats to be imported for use in a GIS. It is an integrated spatial ETL (extract, transform, and load) toolset that runs within the geoprocessing framework using Safe Software's FME technology. It enables you to integrate data from multiple sources and formats, use that data with geoprocessing tools, and even publish it with ArcGIS Server.
I recently tested the Data Interoperability Extension in ArcGIS Pro and was thrilled with the results. Read about how to install and authorize the extension here. The extension does many things, but one that is particularly useful is that the extension creates a toolbox directly in ArcGIS Pro (graphic below). I used this toolbox's Quick Import tool to import a SDTS Format DLG (USGS Digital Line Graph) file directly to a file geodatabase. The tool, like other ArcGIS Pro geoprocessing tools, walked me right through the process: I used Data Interoperability > Quick Import > pointed to my DLG files > named the resulting gdb (file geodatabase). Once imported, I was then able to work with my hydrography, hypsography, roads, boundaries, and other data.
DLG files have existed since the early 1990s. Why are we still working with them? The reasons include that (1) they are dated but still useful vector data sets; (2) many geospatial data portals still host data only in this format, such as the USGS Earth Explorer. See below for step-by-step instructions with screen shots and I have created a video about this process here.
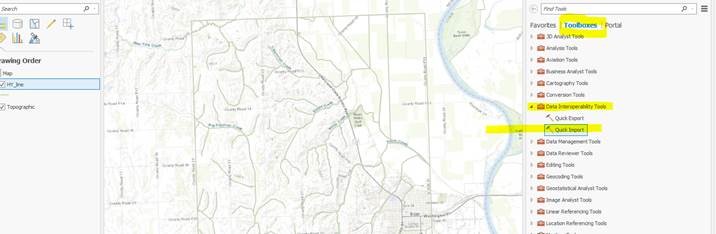
1. Use Toolboxes > Data Interoperability Tools > Quick Import, as shown above.
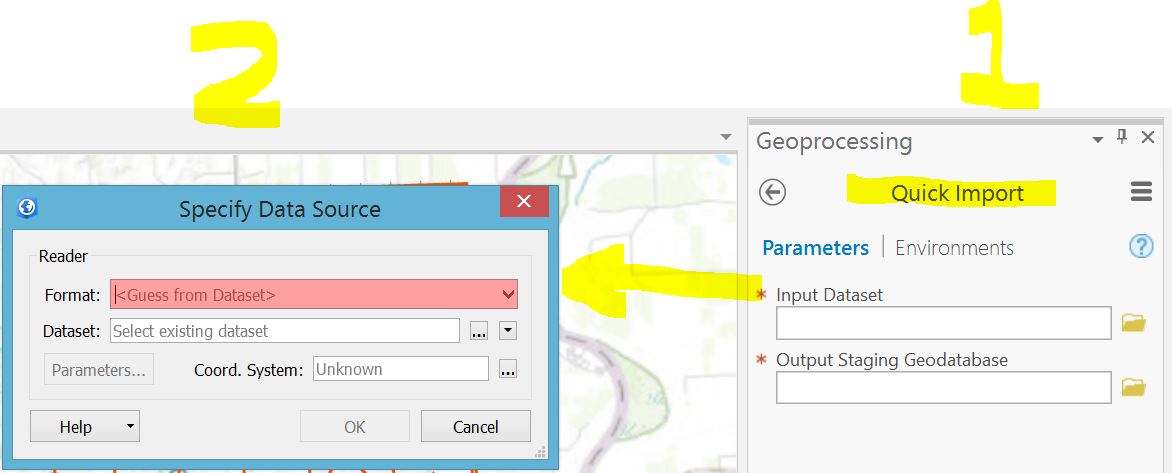
2. Using QuickImport pulls up a "specify data source" dialog box, as shown above.
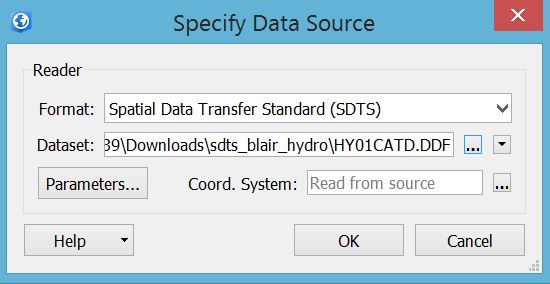
3. In the specify data source dialog box, use "find other source" and then specify SDTS format.
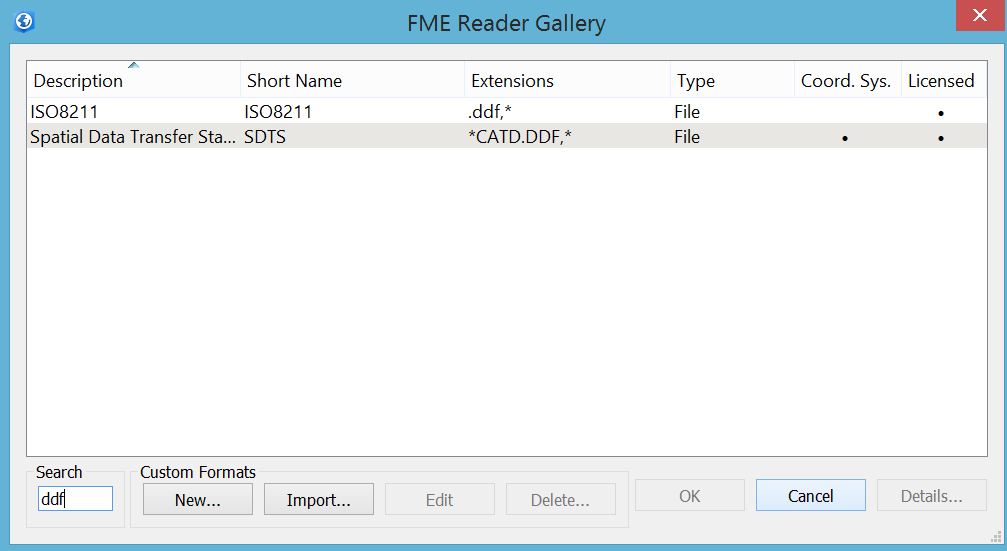
4. Selecting SDTS format.
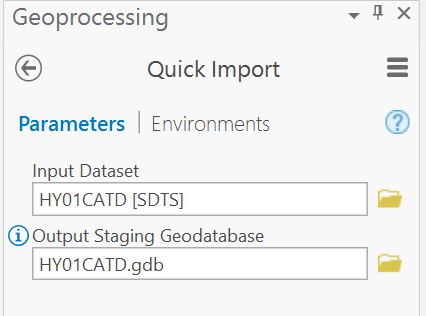
5. Pointing to the SDTS file (after it has been unzipped and un-TAR'd) and saving it into a geodatabase.
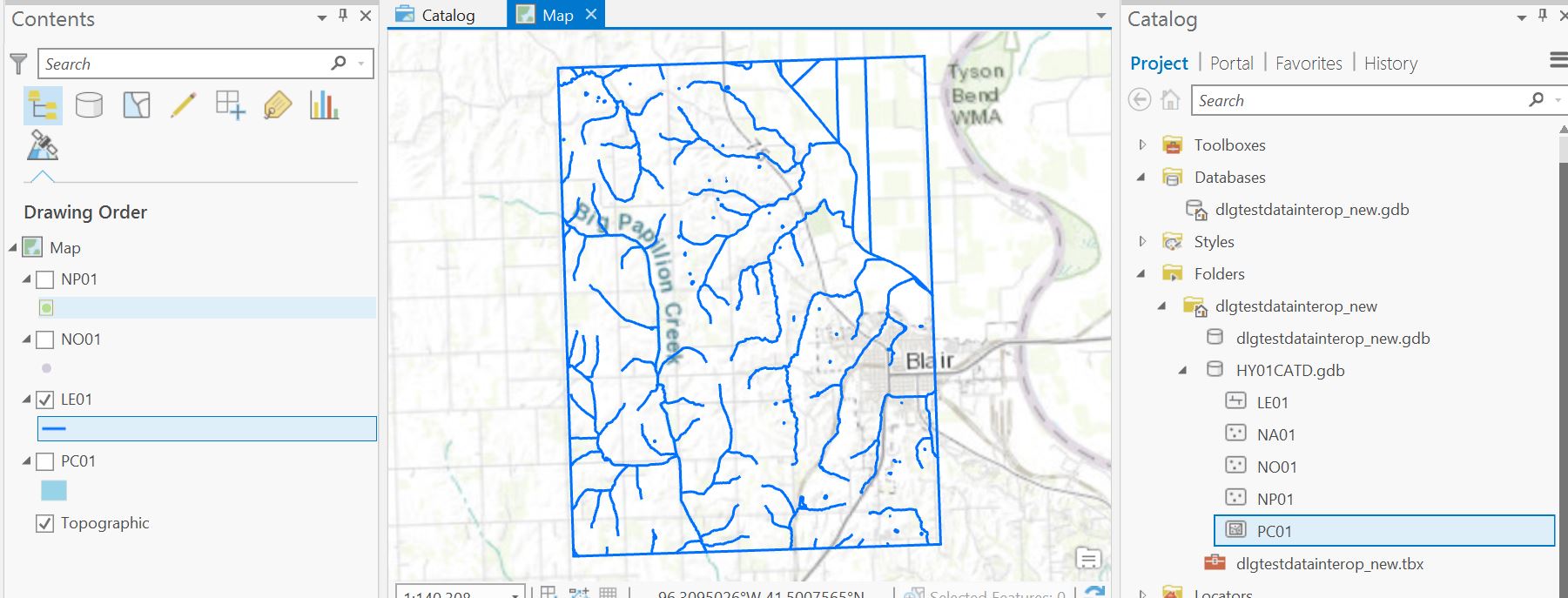
6. Once the file has been imported into a geodatabase, it can be added to a new map in ArcGIS Pro. The data is now ready for use, as shown for this hydrography example, above.
UPDATE JULY 2019: I have created a video about this process here.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
Administration
78 -
Announcements
80 -
Career & Tech Ed
1 -
Curriculum-Learning Resources
258 -
Education Facilities
24 -
Events
72 -
GeoInquiries
1 -
Higher Education
595 -
Informal Education
281 -
Licensing Best Practices
91 -
National Geographic MapMaker
33 -
Pedagogy and Education Theory
225 -
Schools (K - 12)
282 -
Schools (K-12)
273 -
Spatial data
35 -
STEM
3 -
Students - Higher Education
245 -
Students - K-12 Schools
129 -
Success Stories
36 -
TeacherDesk
1 -
Tech Tips
118
- « Previous
- Next »