- Home
- :
- All Communities
- :
- Developers
- :
- Python
- :
- Python Questions
- :
- Re: Exporting Records to .CSV. Problem with Comma...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Exporting Records to .CSV. Problem with Comma data offsets to another field - CODE INCLUDED
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
I have a python script tool that exports records from a feature layer using an (area of interest - aoi). The tool works well, but the problem is that if I have a comma in text in one of the field records, it will break the text after the comma and move it to the next field. The shown below that are highlighted in yellow show records that are offset.
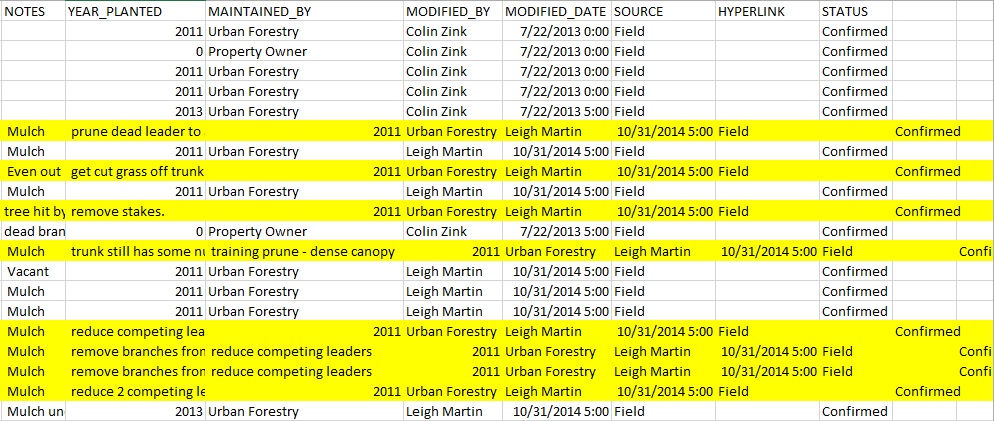
I am attaching the toolbox along with the script. Is there a way I can fix this issue? I didn't get any help from ESRI. They just forwarded me some links, but I figure I can get some assistance from here.
Here is a copy of the toolbox and script as an attachment:
Here is the script code itself:
<CODE>
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
This script will convert a table to an excel spreadsheet. If the third-party
module xlwt is available, it will use that. Otherwise, it will fall back to
CSV.
'''
# **********************************************************************
# * 01. Import arcpy Module *
# **********************************************************************
import arcpy
import os
import zipfile
# **********************************************************************
# * 02. Variable Descriptions *
# **********************************************************************
# Variable Definition
#
# InputDataset Dataset used for input.
# DataDescription Described properties of the input dataset.
# FieldNames Field names from table.
# FileFormat File format of output either CSV or XLS.
# SelectedFeatures Features that are selected from input dataset.
# OutputFile Name of the output file.
# **********************************************************************
# * 03. Prepare Data for Table *
# **********************************************************************
def get_ID_message(ID):
return re.sub('%1|%2', '%s', arcpy.GetIDMessage(ID))
def zipUpFolder(folder, outZipFile):
# zip the data
try:
zip = zipfile.ZipFile(outZipFile, 'w', zipfile.ZIP_DEFLATED)
zipws(unicode(folder), zip, 'CONTENTS_ONLY')
zip.close()
except RuntimeError:
# Delete zip file if exists
if os.path.exists(outZipFile):
os.unlink(outZipFile)
zip = zipfile.ZipFile(outZipFile, 'w', zipfile.ZIP_STORED)
zipws(unicode(folder), zip, 'CONTENTS_ONLY')
zip.close()
#Message' Unable to compress zip file contents.'
arcpy.AddWarning(get_ID_message(86133))
def zipws(path, zip, keep):
path = os.path.normpath(path)
# os.walk visits every subdirectory, returning a 3-tuple
# of directory name, subdirectories in it, and filenames
# in it.
for (dirpath, dirnames, filenames) in os.walk(path):
# Iterate over every filename
for file in filenames:
# Ignore .lock files
if not file.endswith('.lock'):
#arcpy.AddMessage('Adding %s...' % os.path.join(path, dirpath, file))
try:
if keep:
zip.write(os.path.join(dirpath, file),
os.path.join(os.path.basename(path), os.path.join(dirpath, file)[len(path)+len(os.sep):]))
else:
zip.write(os.path.join(dirpath, file),
os.path.join(dirpath[len(path):], file))
except Exception as e:
#Message ' Error adding %s: %s'
arcpy.AddWarning(get_ID_message(86134) % (file, e[0]))
return None
def createFolderInScratch(folderName):
# create the folders necessary for the job
folderPath = arcpy.CreateUniqueName(folderName, arcpy.env.scratchFolder)
arcpy.CreateFolder_management(arcpy.env.scratchFolder, os.path.basename(folderPath))
return folderPath
# Returns a list of column names and an iterator over the same columns
def header_and_iterator(InputDataset):
# Describe Properties of Input Dataset
DataDescription = arcpy.Describe(InputDataset)
# Field Name Definitions
FieldNames = [f.name for f in DataDescription.fields if f.type not in ['Geometry', 'Raster', 'Blob']]
def iterator_for_feature():
cursor = arcpy.SearchCursor(InputDataset)
row = cursor.next()
while row:
yield [getattr(row, col) for col in FieldNames]
row = cursor.next()
del row, cursor
return FieldNames, iterator_for_feature()
def export_to_xls(dataset, output):
# Attempt to output to an XLS file. If xmlwt is not available, fall back
# to CSV. XLWT can be downloaded from http://pypi.python.org/pypi/xlwt
try:
import xlwt
except ImportError:
arcpy.AddError('import of xlwt module failed')
return
header, rows = header_and_iterator(dataset)
# Make spreadsheet
workbook = xlwt.Workbook()
worksheet = workbook.add_sheet(os.path.split(dataset)[1])
#Set Up Header Row and Freeze Panes
header_style = xlwt.easyxf('font: bold on; align: horiz center')
for index, colheader in enumerate(header):
worksheet.write(0, index, colheader.replace('.','_'))
worksheet.set_panes_frozen(True)
worksheet.set_horz_split_pos(1)
worksheet.set_remove_splits(True)
# Write Rows
for rowidx, row in enumerate(rows):
for colindex, col in enumerate(row):
worksheet.write(rowidx+1, colindex, col)
# Completed Workbook
workbook.save(output)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# ***********************************
# * 01. Input Parameters *
# ***********************************
InputDataset = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0) # Input Dataset
aoi = arcpy.GetParameter(1) # Select Area of Interest
FileFormat = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(2) # Output format (CSV or XLS)
OutputFolder = createFolderInScratch('FlatFiles')
OutputZipFile = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(3)
for i,ds in enumerate(InputDataset.split(';')):
# ***********************************
# * 02. Select Dataset By Location *
# ***********************************
arcpy.SelectLayerByLocation_management(ds, 'INTERSECT', aoi)
# Selected Features from Input Dataset
SelectedFeatures = arcpy.MakeFeatureLayer_management(ds)
# ***********************************
# * 03. Format *
# ***********************************
# Comma Separated Values (CSV)
if FileFormat == 'CSV':
fields = ''
for field in arcpy.ListFields(SelectedFeatures):
if field.name.lower() not in ['shape']:
fields = fields + field.name + ';'
fields = fields.rstrip(';')
arcpy.AddMessage('Export to CSV')
# Create CSV File
OutputFile = os.path.join(OutputFolder,'c%s_%s.csv' % (str(i).zfill(2), ds.split(os.sep)[-1]))
arcpy.ExportXYv_stats(SelectedFeatures,fields,'COMMA',OutputFile,'ADD_FIELD_NAMES')
# Excel File (XLS)
elif FileFormat == 'XLS':
try:
# Create XLS File
OutputFile = os.path.join(OutputFolder,'x%s_%s.xls' % (str(i).zfill(2), ds.split(os.sep)[-1]))
export_to_xls(ds, OutputFile)
except:
import traceback
arcpy.AddError(traceback.format_exc())
else:
raise ValueError('Don\'t know how to export to %r' % FileFormat)
zipUpFolder(OutputFolder, OutputZipFile)
</CODE>
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
Well, that is the format for csv files. You could do some fancy checking and replacing. It looks like from your example that the first intended field is the problem one. You could check if the next value is a year, and if not, replace the comma with a zero length string. That could be prone to error, and you may have the same problem in other fields anyway.
It might be easier to make it a tab delimited or fixed length file. That's what I'd look at, anyway.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
you could use the python csv library to create the file.
13.1. csv — CSV File Reading and Writing — Python 2.7.8 documentation
using a search cursor to format your data appropriately.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
I think the problem with that would be in the formatting of data. There are potentially n number of commas in n number of fields. Not to say it couldn't be done, but it wouldn't be a very efficient process.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
If it were me I would fix the datasource first. I could understand a comment field that I *MIGHT* allow commas into it, but probably not because it leads to situations you are in now. So fix the thing that is creating the .csv datasource so that it doesn't allow commas to be inserted. That'd be the optimal thing to do.
If not an option then I'd have a separate process that ran to removes commas and convert them into tabs instead. You will still have to do a bunch of gymnastics to find the specific scenario(s) that you want to use to do the replace.
...which is why it's best to juts fix the source data.
I have a python script tool that exports records from a feature layer using an (area of interest - aoi). The tool works well, but the problem is that if I have a comma in text in one of the field records
This is where I'd focus my first effort. When it's a Feature Class (before you run your tool), remove any commas in any of the fields. But again, why are you letting them into the data in the first place? Control that process and you don't need to deal with this problem.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
I agree with @Dallas Shearer. You can use the Python csv library.
The CSV format allows for escaping special characters, so you can have commas in a field. You would quote that field, as in:
field 1, "This, field has, commas", Field 3
There is a way to handle fields containing quotes as well. It gets a little messy if you have an assortment of such punctuation, but the csv library handles it for you.
Here's a couple of links:
Writing Escape Characters to a Csv File in Python - Stack Overflow
java - How to escape comma and double quote at same time for CSV file? - Stack Overflow
One of the contributors to one of those threads also had a good suggestion: If you want your CSV to be compatible with Excel, take one of those strings, copy it into Excel and save it out as CSV. Then you will know how Excel wants it formatted.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
In similar situations in the past, I just resorted to using the pipe symbol or vertical bar as the field separator. Although I have seen crazy data where people use commas, colons, semicolons, and slashes in places they shouldn't be; I seldom run across people using vertical bars in free-form text.