- Home
- :
- All Communities
- :
- Industries
- :
- Gas and Pipeline
- :
- Gas and Pipeline Questions
- :
- Can I label a points layer perpendicular to a line...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Can I label a points layer perpendicular to a line layer?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
I have a points layer (Electrical Transmission structures) and a Transmission line layer. The points layer sits on top of the line layer and because the line layer changes direction all the time it is hard to label the points layer sometimes. What I would like to do is label the points layer perpendicular to the line layer.
Does anyone have an answer for me?
Solved! Go to Solution.
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
It would be important to know what software you are using (and the version). Are you using desktop (Pro or ArcMap) or ArcGIS Online?
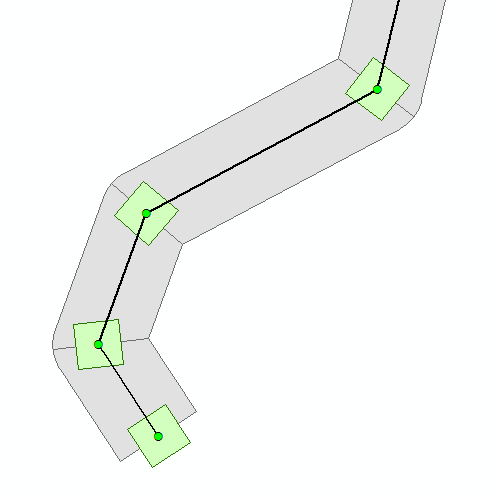
In case of Desktop, you could create a script to generate a field with the rotation based on the bisector. A few years ago I created a tool to define service areas of transmission tower applying the rotation based on the bisector (the green polygons in the image below):
The rotation determined by the tool could be written to the transmission towers and those can be used to define the rotation of the label. See the code below. The angles are determined on lines 51, 73 and 93.
import arcpy
def main():
import os
arcpy.env.overwriteOutput = True
# input fc
fc = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0) # r'C:\...\data.gdb\Torres'
fld_label = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(1) # 'LABEL'
fld_orden = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(2) # 'orden'
buf = arcpy.GetParameter(3) # 20m servidumbre
fc_out = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(4) # poligonos de servidumbre
# spatial reference
sr = arcpy.Describe(fc).spatialReference
# dicts, listado para orden
arcpy.AddMessage('Generar dictionarios con coordenadas, labels y orden...')
flds = (fld_orden, 'SHAPE@')
dct_crds = {r[0]: r[1] for r in arcpy.da.SearchCursor(fc, flds)}
flds = (fld_orden, fld_label)
dct_lbl = {r[0]: r[1] for r in arcpy.da.SearchCursor(fc, flds)}
# create list of points and order list
arcpy.AddMessage('Ordenar torres...')
lst_ptgs = [pntg for orden, pntg in sorted(dct_crds.items())]
lst_orden = sorted(dct_crds.keys())
# create output featureclass
arcpy.AddMessage('Crear featureclass de salida...')
ws, fc_name = os.path.split(fc_out)
arcpy.CreateFeatureclass_management(ws, fc_name, "POLYGON", None, None, None, sr)
# add fields
arcpy.AddField_management(fc_out, fld_label, "TEXT", None, None, 50)
flds_out = ('SHAPE@', fld_label)
# empty lists for output features
lst_puntos = []
lst_lineas = []
lst_poligonos = []
# start insert cursor
arcpy.AddMessage('Recorrer torres...')
with arcpy.da.InsertCursor(fc_out, flds_out) as curs:
# first polygon
if len(lst_ptgs) >= 2:
pntg_1 = lst_ptgs[0]
pntg_2 = lst_ptgs[1]
angle_12 = getAngle(pntg_1, pntg_2)
cut_line = createPerpendicularCutLine(pntg_1, angle_12, buf, sr)
# create polygon
polygon = createServidumbre(pntg_1, cut_line, buf, sr)
# generate and insert output row
lbl1 = dct_lbl[lst_orden[0]]
arcpy.AddMessage(' - procesar: {0}'.format(lbl1))
curs.insertRow((polygon, lbl1, ))
# intermediate polygons
for i in range(1, len(lst_ptgs) - 1):
# read points
pntg_a = lst_ptgs[i - 1]
pntg_1 = lst_ptgs[i]
pntg_2 = lst_ptgs[i + 1]
# get angles and bearings
angle_1a = getAngle(pntg_1, pntg_a)
angle_12 = getAngle(pntg_1, pntg_2)
bearing_l = (angle_1a + angle_12) / 2.0
# create cut lines
cut_line = createCutLine(pntg_1, bearing_l, buf, sr)
# cut polygon
polygon = createServidumbre(pntg_1, cut_line, buf, sr)
# generate and insert output row
lbl1 = dct_lbl[lst_orden[i]]
arcpy.AddMessage(' - procesar: {0}'.format(lbl1))
curs.insertRow((polygon, lbl1, ))
# last polygon
if len(lst_ptgs) >= 2:
pntg_1 = lst_ptgs[len(lst_ptgs) - 2]
pntg_2 = lst_ptgs[len(lst_ptgs) - 1]
# get angles and bearings
angle_21 = getAngle(pntg_2, pntg_1)
cut_line = createPerpendicularCutLine(pntg_2, angle_21, buf, sr)
# cut polygon
polygon = createServidumbre(pntg_2, cut_line, buf, sr)
# generate and insert output row
lbl1 = dct_lbl[lst_orden[len(lst_ptgs) - 2]]
arcpy.AddMessage(' - procesar: {0}'.format(lbl1))
curs.insertRow((polygon, lbl1, ))
arcpy.AddMessage('Listo...')
def createServidumbre(pntg, cut_line, servidumbre, sr):
'''
Create rectangle using the cutline
and the size of the servidumbre
'''
angle_cut_line = getAngleLine(cut_line)
tmp_pntg1 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle_cut_line, servidumbre / 2.0, 'PLANAR')
tmp_pntg2 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle_cut_line + 180, servidumbre / 2.0, 'PLANAR')
# create corner points
pntg1a = tmp_pntg1.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle_cut_line - 90, servidumbre / 2.0, 'PLANAR')
pntg1b = tmp_pntg1.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle_cut_line + 90, servidumbre / 2.0, 'PLANAR')
pntg2a = tmp_pntg2.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle_cut_line + 90, servidumbre / 2.0, 'PLANAR')
pntg2b = tmp_pntg2.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle_cut_line - 90, servidumbre / 2.0, 'PLANAR')
polygon = arcpy.Polygon(arcpy.Array([pntg1a.firstPoint, pntg1b.firstPoint,
pntg2a.firstPoint, pntg2b.firstPoint, pntg1a.firstPoint]), sr)
return polygon
def getAngleLine(line):
pntg1 = arcpy.PointGeometry(line.firstPoint, line.spatialReference)
pntg2 = arcpy.PointGeometry(line.lastPoint, line.spatialReference)
return getAngle(pntg1, pntg2)
def createPerpendicularCutLine(pntg, angle, dist, sr):
pntg_cut_1 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle - 90, dist * 2.0, 'PLANAR')
pntg_cut_2 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle + 90, dist * 2.0, 'PLANAR')
cut_line = arcpy.Polyline(arcpy.Array([pntg_cut_1.firstPoint, pntg_cut_2.firstPoint]), sr)
return cut_line
def createCutLine(pntg, bearing1, buf, sr):
bearing2 = bearing1 + 180
pntg_cut_1 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(bearing1, buf * 10.0, 'PLANAR')
pntg_cut_2 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(bearing2, buf * 10.0, 'PLANAR')
cut_line = arcpy.Polyline(arcpy.Array([pntg_cut_1.firstPoint, pntg_cut_2.firstPoint]), sr)
return cut_line
def createLine(pntg1, pntg2, sr):
return arcpy.Polyline(arcpy.Array([pntg1.firstPoint, pntg2.firstPoint]), sr)
def getAngle(pntg1, pntg2):
return pntg1.angleAndDistanceTo(pntg2, method='PLANAR')[0]
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
It would be important to know what software you are using (and the version). Are you using desktop (Pro or ArcMap) or ArcGIS Online?
In case of Desktop, you could create a script to generate a field with the rotation based on the bisector. A few years ago I created a tool to define service areas of transmission tower applying the rotation based on the bisector (the green polygons in the image below):

The rotation determined by the tool could be written to the transmission towers and those can be used to define the rotation of the label. See the code below. The angles are determined on lines 51, 73 and 93.
import arcpy
def main():
import os
arcpy.env.overwriteOutput = True
# input fc
fc = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0) # r'C:\...\data.gdb\Torres'
fld_label = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(1) # 'LABEL'
fld_orden = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(2) # 'orden'
buf = arcpy.GetParameter(3) # 20m servidumbre
fc_out = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(4) # poligonos de servidumbre
# spatial reference
sr = arcpy.Describe(fc).spatialReference
# dicts, listado para orden
arcpy.AddMessage('Generar dictionarios con coordenadas, labels y orden...')
flds = (fld_orden, 'SHAPE@')
dct_crds = {r[0]: r[1] for r in arcpy.da.SearchCursor(fc, flds)}
flds = (fld_orden, fld_label)
dct_lbl = {r[0]: r[1] for r in arcpy.da.SearchCursor(fc, flds)}
# create list of points and order list
arcpy.AddMessage('Ordenar torres...')
lst_ptgs = [pntg for orden, pntg in sorted(dct_crds.items())]
lst_orden = sorted(dct_crds.keys())
# create output featureclass
arcpy.AddMessage('Crear featureclass de salida...')
ws, fc_name = os.path.split(fc_out)
arcpy.CreateFeatureclass_management(ws, fc_name, "POLYGON", None, None, None, sr)
# add fields
arcpy.AddField_management(fc_out, fld_label, "TEXT", None, None, 50)
flds_out = ('SHAPE@', fld_label)
# empty lists for output features
lst_puntos = []
lst_lineas = []
lst_poligonos = []
# start insert cursor
arcpy.AddMessage('Recorrer torres...')
with arcpy.da.InsertCursor(fc_out, flds_out) as curs:
# first polygon
if len(lst_ptgs) >= 2:
pntg_1 = lst_ptgs[0]
pntg_2 = lst_ptgs[1]
angle_12 = getAngle(pntg_1, pntg_2)
cut_line = createPerpendicularCutLine(pntg_1, angle_12, buf, sr)
# create polygon
polygon = createServidumbre(pntg_1, cut_line, buf, sr)
# generate and insert output row
lbl1 = dct_lbl[lst_orden[0]]
arcpy.AddMessage(' - procesar: {0}'.format(lbl1))
curs.insertRow((polygon, lbl1, ))
# intermediate polygons
for i in range(1, len(lst_ptgs) - 1):
# read points
pntg_a = lst_ptgs[i - 1]
pntg_1 = lst_ptgs[i]
pntg_2 = lst_ptgs[i + 1]
# get angles and bearings
angle_1a = getAngle(pntg_1, pntg_a)
angle_12 = getAngle(pntg_1, pntg_2)
bearing_l = (angle_1a + angle_12) / 2.0
# create cut lines
cut_line = createCutLine(pntg_1, bearing_l, buf, sr)
# cut polygon
polygon = createServidumbre(pntg_1, cut_line, buf, sr)
# generate and insert output row
lbl1 = dct_lbl[lst_orden[i]]
arcpy.AddMessage(' - procesar: {0}'.format(lbl1))
curs.insertRow((polygon, lbl1, ))
# last polygon
if len(lst_ptgs) >= 2:
pntg_1 = lst_ptgs[len(lst_ptgs) - 2]
pntg_2 = lst_ptgs[len(lst_ptgs) - 1]
# get angles and bearings
angle_21 = getAngle(pntg_2, pntg_1)
cut_line = createPerpendicularCutLine(pntg_2, angle_21, buf, sr)
# cut polygon
polygon = createServidumbre(pntg_2, cut_line, buf, sr)
# generate and insert output row
lbl1 = dct_lbl[lst_orden[len(lst_ptgs) - 2]]
arcpy.AddMessage(' - procesar: {0}'.format(lbl1))
curs.insertRow((polygon, lbl1, ))
arcpy.AddMessage('Listo...')
def createServidumbre(pntg, cut_line, servidumbre, sr):
'''
Create rectangle using the cutline
and the size of the servidumbre
'''
angle_cut_line = getAngleLine(cut_line)
tmp_pntg1 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle_cut_line, servidumbre / 2.0, 'PLANAR')
tmp_pntg2 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle_cut_line + 180, servidumbre / 2.0, 'PLANAR')
# create corner points
pntg1a = tmp_pntg1.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle_cut_line - 90, servidumbre / 2.0, 'PLANAR')
pntg1b = tmp_pntg1.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle_cut_line + 90, servidumbre / 2.0, 'PLANAR')
pntg2a = tmp_pntg2.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle_cut_line + 90, servidumbre / 2.0, 'PLANAR')
pntg2b = tmp_pntg2.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle_cut_line - 90, servidumbre / 2.0, 'PLANAR')
polygon = arcpy.Polygon(arcpy.Array([pntg1a.firstPoint, pntg1b.firstPoint,
pntg2a.firstPoint, pntg2b.firstPoint, pntg1a.firstPoint]), sr)
return polygon
def getAngleLine(line):
pntg1 = arcpy.PointGeometry(line.firstPoint, line.spatialReference)
pntg2 = arcpy.PointGeometry(line.lastPoint, line.spatialReference)
return getAngle(pntg1, pntg2)
def createPerpendicularCutLine(pntg, angle, dist, sr):
pntg_cut_1 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle - 90, dist * 2.0, 'PLANAR')
pntg_cut_2 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle + 90, dist * 2.0, 'PLANAR')
cut_line = arcpy.Polyline(arcpy.Array([pntg_cut_1.firstPoint, pntg_cut_2.firstPoint]), sr)
return cut_line
def createCutLine(pntg, bearing1, buf, sr):
bearing2 = bearing1 + 180
pntg_cut_1 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(bearing1, buf * 10.0, 'PLANAR')
pntg_cut_2 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(bearing2, buf * 10.0, 'PLANAR')
cut_line = arcpy.Polyline(arcpy.Array([pntg_cut_1.firstPoint, pntg_cut_2.firstPoint]), sr)
return cut_line
def createLine(pntg1, pntg2, sr):
return arcpy.Polyline(arcpy.Array([pntg1.firstPoint, pntg2.firstPoint]), sr)
def getAngle(pntg1, pntg2):
return pntg1.angleAndDistanceTo(pntg2, method='PLANAR')[0]
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
Desktop 10.5.1 or ArcGIS Pro 2.1.1
I am not a big time programmer.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
Is it possible for you to share a sample of the data? I could have a look if I can adjust the script to what you need. The result would be an additional field with the rotation in the point layer.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
I have to look into it, but it might be possible. Which layer do you want? Points or Lines.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
It could (or should) be both. Or if the points follow the order (sequence) of the line one could determine the angles of the lines based on only the points. Otherwise, one has to determine the angles of both line parts based on the line. It also matter is the line is a single line, or each segment from tower to tower is a feature. Would be could to see the data to understand those aspects, since it determines how the code should be changed.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
Hi, @XanderBakker !
Could I get a help with this script?
I have the same queastion as @Paul 😕
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
Hi @GIS_Rookie ,
Then I suppose I have to reply with a question similar to the one I asked Paul. Do you have a sample of data that you can share? That will help understand what you have and what you are looking for.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
Hi @GIS_Rookie ,
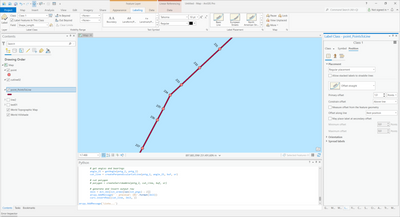
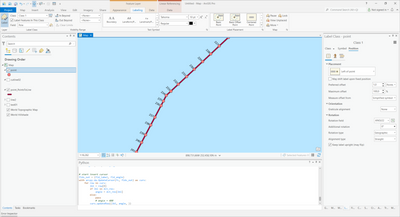
Thanks for sharing the sample of data. There are a couple of ways you can proceed. I created a line featureclass using the cut lines and changed it a bit to have it align to the left and I included the pole information for labeling. Have a look at the result below:
See below the Python code I used (in the Python window of ArcGIS Pro):
def getAngleLine(line):
pntg1 = arcpy.PointGeometry(line.firstPoint, line.spatialReference)
pntg2 = arcpy.PointGeometry(line.lastPoint, line.spatialReference)
return getAngle(pntg1, pntg2)
def createPerpendicularCutLine(pntg, angle, dist, sr):
pntg_cut_1 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle - 90, dist * 2.0, 'PLANAR')
pntg_cut_2 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(angle + 90, dist * 2.0, 'PLANAR')
cut_line = arcpy.Polyline(arcpy.Array([pntg_cut_1.firstPoint, pntg_cut_2.firstPoint]), sr)
return cut_line
def createCutLine(pntg, bearing1, buf, sr):
bearing2 = bearing1 + 180
pntg_cut_1 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(bearing1, buf * 1.5, 'PLANAR')
pntg_cut_2 = pntg.pointFromAngleAndDistance(bearing2, buf * 0, 'PLANAR')
cut_line = arcpy.Polyline(arcpy.Array([pntg_cut_1.firstPoint, pntg_cut_2.firstPoint]), sr)
return cut_line
def createLine(pntg1, pntg2, sr):
return arcpy.Polyline(arcpy.Array([pntg1.firstPoint, pntg2.firstPoint]), sr)
def getAngle(pntg1, pntg2):
return pntg1.angleAndDistanceTo(pntg2, method='PLANAR')[0]
import os
arcpy.env.overwriteOutput = True
# input fc
fc = r'D:\GeoNet\TransmissionLabel\point.shp'
fld_label = 'Pole'
fld_orden = 'Pole'
buf = 20
fc_out = r'D:\GeoNet\TransmissionLabel\cutline02.shp'
# spatial reference
sr = arcpy.Describe(fc).spatialReference
# dicts, listado para orden
flds = (fld_orden, 'SHAPE@')
dct_crds = {r[0]: r[1] for r in arcpy.da.SearchCursor(fc, flds)}
flds = (fld_orden, fld_label)
dct_lbl = {r[0]: r[1] for r in arcpy.da.SearchCursor(fc, flds)}
# create list of points and order list
lst_ptgs = [pntg for orden, pntg in sorted(dct_crds.items())]
lst_orden = sorted(dct_crds.keys())
# create output featureclass
ws, fc_name = os.path.split(fc_out)
arcpy.CreateFeatureclass_management(ws, fc_name, "POLYLINE", None, None, None, sr)
# add fields
arcpy.AddField_management(fc_out, fld_label, "TEXT", None, None, 50)
flds_out = ('SHAPE@', fld_label)
# empty lists for output features
lst_puntos = []
lst_lineas = []
lst_polylines = []
# start insert cursor
with arcpy.da.InsertCursor(fc_out, flds_out) as curs:
# first polygon
if len(lst_ptgs) >= 2:
pntg_1 = lst_ptgs[0]
pntg_2 = lst_ptgs[1]
angle_12 = getAngle(pntg_1, pntg_2)
cut_line = createPerpendicularCutLine(pntg_1, angle_12, buf, sr)
# generate and insert output row
lbl1 = dct_lbl[lst_orden[0]]
arcpy.AddMessage(' - procesar: {0}'.format(lbl1))
curs.insertRow((cut_line, lbl1, ))
# intermediate polygons
for i in range(1, len(lst_ptgs) - 1):
# read points
pntg_a = lst_ptgs[i - 1]
pntg_1 = lst_ptgs[i]
pntg_2 = lst_ptgs[i + 1]
# get angles and bearings
angle_1a = getAngle(pntg_1, pntg_a)
angle_12 = getAngle(pntg_1, pntg_2)
bearing_l = (angle_1a + angle_12) / 2.0
# create cut lines
cut_line = createCutLine(pntg_1, bearing_l, buf, sr)
# generate and insert output row
lbl1 = dct_lbl[lst_orden[i]]
arcpy.AddMessage(' - procesar: {0}'.format(lbl1))
curs.insertRow((cut_line, lbl1, ))
# last polygon
if len(lst_ptgs) >= 2:
pntg_1 = lst_ptgs[len(lst_ptgs) - 2]
pntg_2 = lst_ptgs[len(lst_ptgs) - 1]
# get angles and bearings
angle_21 = getAngle(pntg_2, pntg_1)
cut_line = createPerpendicularCutLine(pntg_2, angle_21, buf, sr)
# generate and insert output row
lbl1 = dct_lbl[lst_orden[len(lst_ptgs) - 2]]
arcpy.AddMessage(' - procesar: {0}'.format(lbl1))
curs.insertRow((cut_line, lbl1, ))
The other way would be to write the angle to the points. This can be achieved like this:
def getAngle(pntg1, pntg2):
return pntg1.angleAndDistanceTo(pntg2, method='PLANAR')[0]
import os
arcpy.env.overwriteOutput = True
# input fc
fc = r'D:\GeoNet\TransmissionLabel\point.shp'
fld_label = 'Pole'
fld_orden = 'Pole'
fld_angle = 'ANGLE2'
buf = 20
# spatial reference
sr = arcpy.Describe(fc).spatialReference
# dicts, listado para orden
flds = (fld_orden, 'SHAPE@')
dct_crds = {r[0]: r[1] for r in arcpy.da.SearchCursor(fc, flds)}
flds = (fld_orden, fld_label)
dct_lbl = {r[0]: r[1] for r in arcpy.da.SearchCursor(fc, flds)}
# create list of points and order list
lst_ptgs = [pntg for orden, pntg in sorted(dct_crds.items())]
lst_orden = sorted(dct_crds.keys())
dct_res = {}
# first polygon
if len(lst_ptgs) >= 2:
pntg_1 = lst_ptgs[0]
pntg_2 = lst_ptgs[1]
angle_12 = getAngle(pntg_1, pntg_2) + 90.0
# generate and insert output row
lbl1 = dct_lbl[lst_orden[0]]
dct_res[lbl1] = angle_12
# intermediate polygons
for i in range(1, len(lst_ptgs) - 1):
# read points
pntg_a = lst_ptgs[i - 1]
pntg_1 = lst_ptgs[i]
pntg_2 = lst_ptgs[i + 1]
# get angles and bearings
angle_1a = getAngle(pntg_1, pntg_a)
angle_12 = getAngle(pntg_1, pntg_2)
bearing_l = (angle_1a + angle_12) / 2.0
# generate and insert output row
lbl1 = dct_lbl[lst_orden[i]]
dct_res[lbl1] = bearing_l
# last polygon
if len(lst_ptgs) >= 2:
pntg_1 = lst_ptgs[len(lst_ptgs) - 2]
pntg_2 = lst_ptgs[len(lst_ptgs) - 1]
# get angles and bearings
angle_21 = getAngle(pntg_2, pntg_1) - 90.0
# generate and insert output row
lbl1 = dct_lbl[lst_orden[len(lst_ptgs) - 2]]
dct_res[lbl1] = angle_21
# start insert cursor
flds_out = (fld_label, fld_angle)
with arcpy.da.UpdateCursor(fc, flds_out) as curs:
for row in curs:
lbl = row[0]
if lbl in dct_res:
angle = dct_res[lbl]
else:
pass
# angle = 400
curs.updateRow((lbl, angle, ))
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
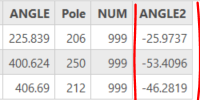
Oh, thank you for quick response 🙂
Second script worked well for me, but I have one queastion about ANGLE2. Is there a way to get positive angle not negative? Example in picture, marked with red.