- Home
- :
- All Communities
- :
- Industries
- :
- Telecommunications
- :
- Telecommunications Blog
- :
- Modernizing OSS/BSS with a Geospatial Systems Appr...
Modernizing OSS/BSS with a Geospatial Systems Approach
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
The state of the telecommunications industry is continually undergoing significant changes, driven by customer and investor expectations, emerging business opportunities, environmental challenges, and new technologies. As enterprise technology advances, the traditional Operations Support Systems (OSS) and Business Support Systems (BSS) frameworks are becoming outdated, necessitating a shift towards more modern and efficient solutions. This transformation is essential for telecom companies to stay competitive, meet the evolving demands of their customers, and enhance operational efficiency. In this blog, we will explore how enterprise geographic information systems (GIS) are contributing to the modernization of the OSS/BSS in the telecommunications industry. We will also discuss the various ArcGIS system patterns and deployment options that are specifically designed for this industry.
A Comprehensive GIS for Telecommunications
A GIS is a powerful technology used to create, manage, analyze, and map various types of data. It is widely recognized as a proven IT technology that enables users to understand patterns, relationships, and geographic context. GIS serves as a foundation for mapping and analysis, supporting business, operational, and scientific workflows across numerous industries, including telecommunications.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend among telecom companies to view GIS as an enterprise system that integrates seamlessly within the IT ecosystem alongside OSS and BSS. This approach allows for comprehensive mapping, geospatial data management, and spatial analytics capabilities throughout the entire organization.
When telecom companies implement GIS as an enterprise system, the extensive functionality of GIS enhances the entire organization’s operations, decision-making processes, and overall efficiency. It enables them to gain valuable insights from OSS/BSS information and geospatial data, optimize network planning and management, improve customer service, and support various other critical workflows.
ArcGIS, an enterprise GIS technology, enables organizations in the telecommunications industry to make informed decisions by connecting maps, apps, data, and people. It provides a comprehensive system that allows users to discover, use, make, and share maps from any device, anywhere, and at any time. One of the key strengths of ArcGIS is its flexibility, which is achieved through various deployment patterns and approaches. These approaches cater to the specific needs and requirements of the telecommunications industry, making it easier for organizations to extend the reach of GIS across their entire enterprise.
What is an ArcGIS System Pattern?
ArcGIS system patterns are abstractions of actual systems, describing the most common types of geospatial systems that organizations implement with ArcGIS software and services. System patterns are typically observed across multiple industries and markets. The goal of system patterns is to help those designing and building IT and GIS systems understand the most common ways ArcGIS capabilities and products are combined into systems that organizations design, deploy, and operate.
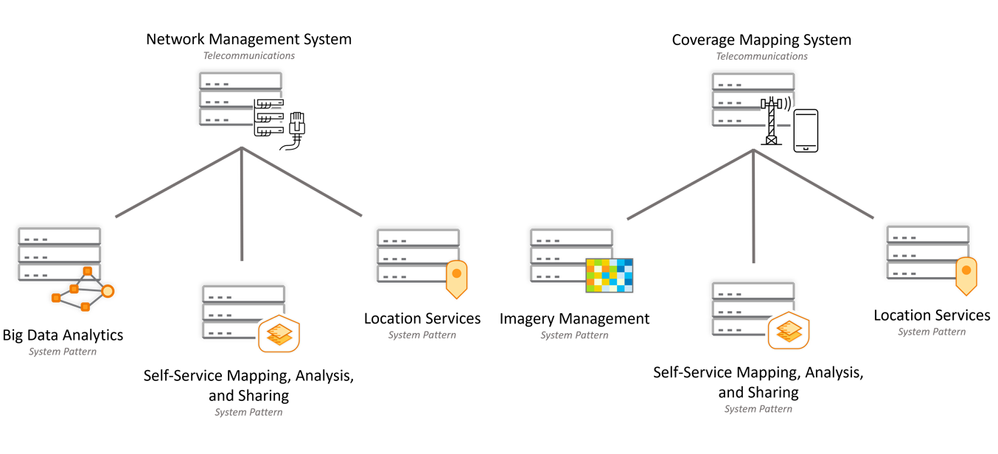
For example, a location services system is used for location-based capabilities including basemaps, geocoding, routing, and spatial analytics, and deliver an organization’s own location-based foundational data services to the enterprise. Some of the core workflows for the location services system are delivering authoritative, foundational geospatial content and capabilities to all the maps, applications, systems, and workflows within an organization. This system pattern may take multiple forms when implemented in an industry-specific context, for example, within a telecom network management system or a telecom coverage mapping system. Some examples of this are shown below.
Common ArcGIS System Patterns in Telecommunications
Self-Service mapping, Analysis, and Sharing Systems are web-centric, services-based systems for self-service creation, sharing, and use of data, maps, and applications. This system pattern empowers individuals and teams to create, share, and use geospatial content without significant technical expertise or GIS knowledge. It also supports self-service spatial analysis. While web-centric, users may interact with it using not only web applications, but also mobile applications. Through these mobile applications users have access to mobile map books and data collection capabilities. This pattern is often how ArcGIS is introduced to an organization and can serve as both an engagement center and a creative engine for the enterprise.
Big Data Analytics Systems are used for analyzing large volumes of geographic and tabular data. This system pattern leverages Apache Spark as the engine for performing large-scale data analytics in batch on distributed compute infrastructure. Spatial and temporal big data analytic results are typically written back to data stores for further downstream analysis, or to other ArcGIS systems for visualization and further geographic analysis. In telecommunications, call record analysis and device performance analysis are examples of big data analysis.
Location Services Systems deliver ready-to-use, location-based services for enterprise-wide and/or public use. This system pattern can support a variety of location-based capabilities including basemaps, places, geocoding, routing, and spatial analytics, and deliver an organization’s own foundational location data services to the enterprise. Location services systems are foundational, often delivering capabilities to other systems within the enterprise.
Imagery Data Management Systems are designed for cataloging and serving large collections of imagery, Lidar, elevation, multidimensional, oriented imagery and/or video at any scale in both 2D and 3D contexts. This system supports cataloging, querying, loading data models and rendering imagery or raster data for enterprise use cases, with access through web services and on-the-fly processing supporting visualization, exploitation, and analysis. This system efficiently unlocks information for use across the many needs of an enterprise organization, meeting users where they are while supporting a vision to scale further into new cloud capabilities.
These four ArcGIS system patterns are the most commonly observed in the telecommunications industry. But as telecom companies continue to adopt GIS technology, more patterns are emerging, and multiple deployments of ArcGIS are being interconnected in the enterprise IT ecosystem.
Deploying Multiple ArcGIS System Patterns
In many cases a single system pattern can be used as the basis for a system. But there are also cases where the needs of a system cannot be met by one system pattern alone; the capabilities from multiple system patterns are required. The decision to implement and integrate two systems or implement a single, composite system may involve many factors, including, but not limited to, reuse of capabilities across the enterprise, deployment, infrastructure, and physical architecture considerations, as well as IT governance practices within the organization.
ArcGIS supports flexible deployment options, enabling you to deploy and manage ArcGIS in a way that aligns best with your organization’s IT environment. These deployment options align with the foundational ArcGIS products and deployment approaches, including:
ArcGIS Online (SaaS)
ArcGIS Enterprise for Windows/Linux (Windows/Linux)
ArcGIS Enterprise for Kubernetes (Kubernetes)
ArcGIS Platform (PaaS)
When considering different deployment options please take into consideration the capabilities supported by foundational products that support them, as there are differences in the functional and non-functional capabilities delivered by the products described above. Depending on the capabilities of a system being deployed, and the architecture requirements of an organization, a telecom company may deploy ArcGIS as a singular system using a singular deployment approach, or as a system of systems leveraging multiple deployment and architecture approaches.
For more information and guidance on selecting a deployment pattern, please explore the ArcGIS system patterns and the choosing ArcGIS architecture components topic of the ArcGIS Well-Architected Framework.
Final Thoughts
As GIS becomes a mission critical enterprise IT system for telecommunications, Esri has designed and built ArcGIS as a comprehensive GIS that supports a variety of patterns of use. Telecom companies deploying ArcGIS should consider the different system and deployment patterns to ensure ArcGIS is architected for success and deployed in a manner that supports all the needs of the business, while operating at a high service-level agreement. Esri's ArcGIS Architecture Center offers a well-architected framework that provides more information on ArcGIS as an enterprise system, as well as architecture best practices. If you are interested in learning more or have any questions, please don't hesitate to reach out to our team.
Resources:
Learn more about ArcGIS use in Telecommunications
Learn more about the ArcGIS Well-Architected Framework
Learn more about Location Management a Key Component in TM Forum’s Open Digital Architecture
Patrick Huls - Solution Engineer Team Lead - Telecommunications
Juan Carlos Tarazona - Solution Architect - Telecommunications
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.