- Home
- :
- All Communities
- :
- Products
- :
- ArcGIS Enterprise
- :
- ArcGIS Enterprise Questions
- :
- ArcGIS Server 10.7.1: How joined machines respond ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
ArcGIS Server 10.7.1: How joined machines respond in case of failure in the main ArcGIS Server machine?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
I couldn’t figure out how joined machines respond in case of failure in the main ArcGIS Server machine due to the fact that services are consumed by links containing the IP of the main ArcGIS Server machine.
For example, if my web mapping application is consuming services from machine (m1) where machine (m2) is joined to it. Now, how the joined machine (m2) can be of advantage if (m1) fails? Do I still need to redirect services consumed in the web mapping application to m2 MANUALLY?
Any help is highly appreciated
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
Hi Abdullah,
You will want to have either the ArcGIS Web Adaptor, or a 3rd party load balancer in front of your multi-machine ArcGIS Server site. The Web Adaptor/Load Balancer will know that one of the servers is down and send the request to the server that is running.
Multiple-machine deployment with ArcGIS Web Adaptor
Multiple-machine deployment with third party load balancer
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
Hi Jake,
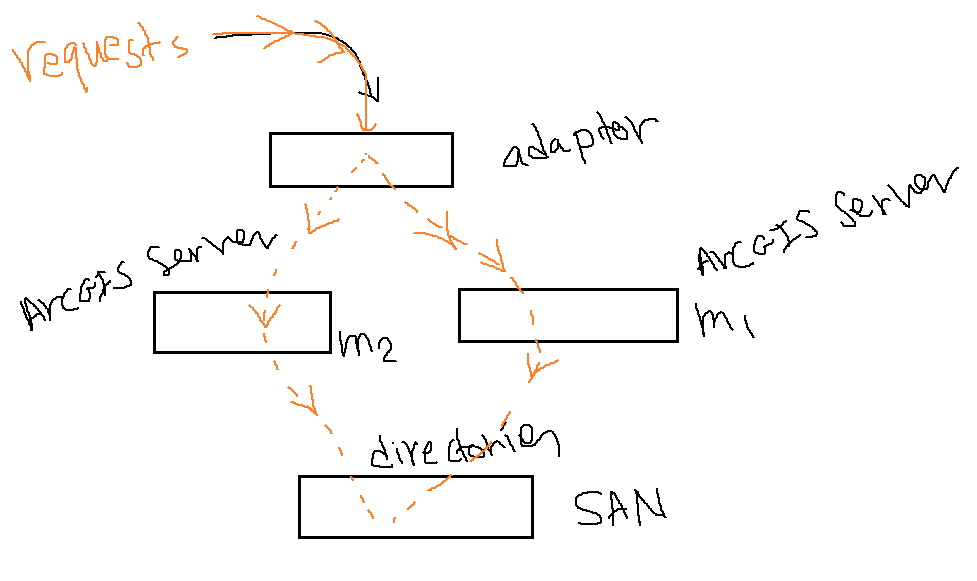
Is it recommended to place the ArcGIS Server Directories Site to a SAN instead of having them stored on the hard drive of the ArcGIS Server machine (m1, for example)? In this case, if the server machine (m1) fails or shut down, then services (that are stored on directories) keep working as they can be approached by the ArcGIS Server installed in the second machine (m2) and joined to m1.
Is this accurate?
Jamal Numan
Geomolg Geoportal for Spatial Information
Ramallah, West Bank, Palestine
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
Jamal NUMAN yes, that is exactly correct. You will also want to place the Configuration Store directory on the SAN in your above example.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
Thanks Jake.
I wonder how this deployment (with adaptor option) should improve the performance. In other words, how can the adaptor work as load balancer and thus distribute loads\requests\traffic optimally? Is this by design?
Jamal Numan
Geomolg Geoportal for Spatial Information
Ramallah, West Bank, Palestine
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
Jamal NUMAN the Web Adaptor will not work as a true load balancer. It will detect if an ArcGIS Server instance is running, but will not distribute the request based on the server load. It will distribute it in a round-robin fashion.
For example, say you execute a GP service that takes 10 mins, the Web Adaptor will send the request to Server1. Then someone adds a service to a web map, this request will be sent to Server2. Another user adds another service to a web map, even though Server1 is under high utilization due to the GP service running, the request is still sent Server1.