In this tutorial, you will take the role of a conservation professional in Puerto Rico, identifying different bioclimatic regions in El Yunque National Forest for conservation efforts to meet targets of the UN Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
You will use bioclimatic data layers and multivariate clustering tools to identify the zones, a process called regionalization. The results can be used to better understand, manage, and conserve key habitats to reduce species extinction, as outlined in GBF Target 4, and to conserve at least 30 percent of terrestrial land (Target 2 and Target 3).
The primary factors that drive species distributions are environmental factors and ecological interactions. To ensure the success of the species, it is crucial to preserve its habitat. However, preserving habitats presents many challenges. Habitats are very complex and consist of interrelated environmental characteristics. To make informed decisions for conservation, it is important to understand the existing habitats, their spatial extent, and their rarity.
Depending on your specific goals and specific locations, you will use different layers, including data from national mapping agencies and your own organization, but many of these layers are freely available online.
The approach outlined in this tutorial is intended to demonstrate some of the data available for conservation, and the tools that you can apply. It is not intended to prescribe a workflow or specific data layers.
In this tutorial, you will act as a GIS analyst who works for a water distribution utility. A new residential development is being built in your service territory and you will use ArcGIS Utility Network to provide the operations, planning, and engineering departments with the information they need to complete the work. Once construction is complete, you will use the editing and validation capabilities of Utility Network to ensure the geographic information system (GIS) accurately reflects the way equipment was constructed in the field.
Along the way, you'll learn how to trace subnetworks, identify affected customers, create and edit utility network features, validate topology, and update subnetworks.

The Public Works Department of the City of Lisle, Illinois, has been using the geometric network to manage its municipal electric network. Your manager has tasked you with exploring the capabilities of a utility network in ArcGIS to model and analyze your network's assets.
To help you get started, a consultant has populated a small subset of your service territory with data from the Electric Utility Network Essentials Foundation. In this tutorial, you'll use this sample data to experiment with the utility network's functionality. You'll perform traces to answer questions about your network, run reports to identify customer count, and perform a service line extension to bring power to a new customer followed by an update subnetwork operation to incorporate this service line into the subnetwork.

Since 2012, delineating catchment areas has become an imperative for National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designated cancer centers. These catchment areas are contiguous geographic areas from which cancer centers draw most of their patient population. They are foundational for planning, resource allocation, engagement, and ensuring equitable access to services.
In this tutorial, you'll create four potential catchment areas for a fictitious cancer center in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, using the following methods:
- Identifying counties adjacent to the county the cancer center is in
- Creating a 60-mile buffer around the cancer center
- Creating a 60-mile driving distance service area around the cancer center
- Identifying the area where the cancer center's core patients live, with outliers excluded
Using infographics and a map series layout, you'll compare the four potential catchment areas so the center's leadership can make an informed decision about which to submit to the NCI.
In 1971, through the National Cancer Act, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Cancer Centers Program was created. This program recognizes and funds leading cancer centers performing state-of-the-art research that deliver cutting-edge treatments to the patients in their service areas, commonly called cancer center catchment areas.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to create a map that visualizes the coverage of National Cancer Institute cancer center catchment areas across the United States, including their designated cancer centers and then further analyze the demographic composition of each catchment area to learn more about the population being served. In the context of health care, catchment areas are the geographic regions where patients are referred to a specific health-care facility or service. This allows for strategic planning and resource allocation for the cancer center facilities to ensure they are serving their patients effectively. Cancer center catchment areas are self-defined geographic areas that each NCI-Designated Cancer Center serves or intends to serve in the research it conducts, communities it engages, and the outreach it performs.
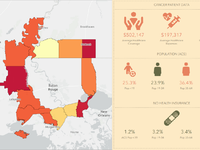
In the United States, the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health, awards grants to support cancer control measures for organizations that meet rigorous standards. The process is highly competitive and achieving the concomitant NCI designation is prestigious. The NCI designation and the grant award continue for five to seven years before renewal is required.
In this tutorial, you will take on the role of analyst as part of the team preparing a renewal application for their NCI sponsored Cancer Center Support Grant. You will examine the current cancer center catchment area for your organization and make plans for strategic expansion of the catchment, knowing that NCI will appreciate your cancer center's effort to serve more people. To share information about the population contained within the catchment, you'll customize an infographic that you can include in your grant application.
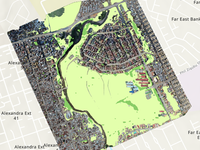
High-resolution land cover layers are valuable tools for mapping and understanding the environment. They provide detailed information about the different types of land cover—such as vegetation, buildings, water bodies, and roads—at a fine-grained spatial resolution. One approach to creating such layers is to use GeoAI applied to drone imagery, classifying the imagery pixels into their corresponding land cover types. While it is possible to train your own deep learning model for this task, you can also take advantage of a pretrained model provided by ArcGIS Living Atlas.
In this tutorial, focused on the Township of Alexandra, South Africa, you'll try out this approach in ArcGIS Pro, with the goal of identifying green spaces and computing their overall surface area. Information about green space distribution is crucial for urban planning, resource allocation, and social development initiatives.

Feral swine (Sus scrofa) are an invasive species that destroy or degrade acres of natural habitat each year, threatening biodiversity and disrupting native species. Their rooting and foraging can also damage agriculture and irrigation systems, and they can carry infectious diseases that pass to domestic cattle. Modeling the distribution of these animals based on observations from iNaturalist can help wildlife and conservation managers track, assess, and contain the destruction.
In this tutorial, you'll focus on two methods for species distribution modeling, Forest-based and Boosted Classification and Regression, and Presence-only Prediction. Both methods can be used individually or in combination to create and assess species distribution.
The approach outlined in this tutorial is intended to demonstrate some of the methods available for species distribution modeling. It is not intended to prescribe a workflow or singular approach to the topic. When using these methods in your work, be sure to apply your own subject matter expertise on the phenomena being modeled to produce the best results.

Whether you work for a commercial company that's trying to start a new business or are part of a local government promoting economic development, or anyone simply trying to understand an area, ArcGIS Business Analyst provides data, tools, and workflows for everyone. Gain access to thousands of demographic and business variables that help in many private and public sector workflows, including expanding to a new business location or promoting economic development. Business Analyst Web App includes an AI assistant—Business Analyst Assistant (Beta). It can be used by new users to learn about the app and existing users for productivity. It can be used to get you started creating a map or as an embedded part of your workflow.
In this tutorial, you are interested in expanding a business that sells pickleball equipment. You will start by creating a map showing the locations of recreation centers and where people have bought more recreation sporting goods than the national average. Using the assistant, you will generate a color-coded map showing pickleball activity to help inform where your next target market should be located.