- Home
- :
- All Communities
- :
- Products
- :
- Imagery and Remote Sensing
- :
- Imagery Blog
- :
- Introducing ready-to-use geospatial deep learning ...
Introducing ready-to-use geospatial deep learning models
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
With the firehose of imagery that’s streaming down daily from a variety of sensors, the need for using AI to automate feature extraction is only increasing. To make sure your organization is prepared, Esri is taking AI to the next level. We are very excited to announce the release of ready-to-use geospatial AI models on the ArcGIS Living Atlas.
Article Overview: Esri is bringing ready-to-use deep learning models to our user community through ArcGIS Online.
To kick it off, we’ve added three models — building footprint extraction and land cover classification from satellite imagery, and another model to classify points representing trees in point cloud datasets.
With the existing capabilities in ArcGIS, you’ve been able to train over a dozen deep learning models on geospatial datasets and derive information products using the ArcGIS API for Python or ArcGIS Pro, and scale up processing using ArcGIS Image Server.
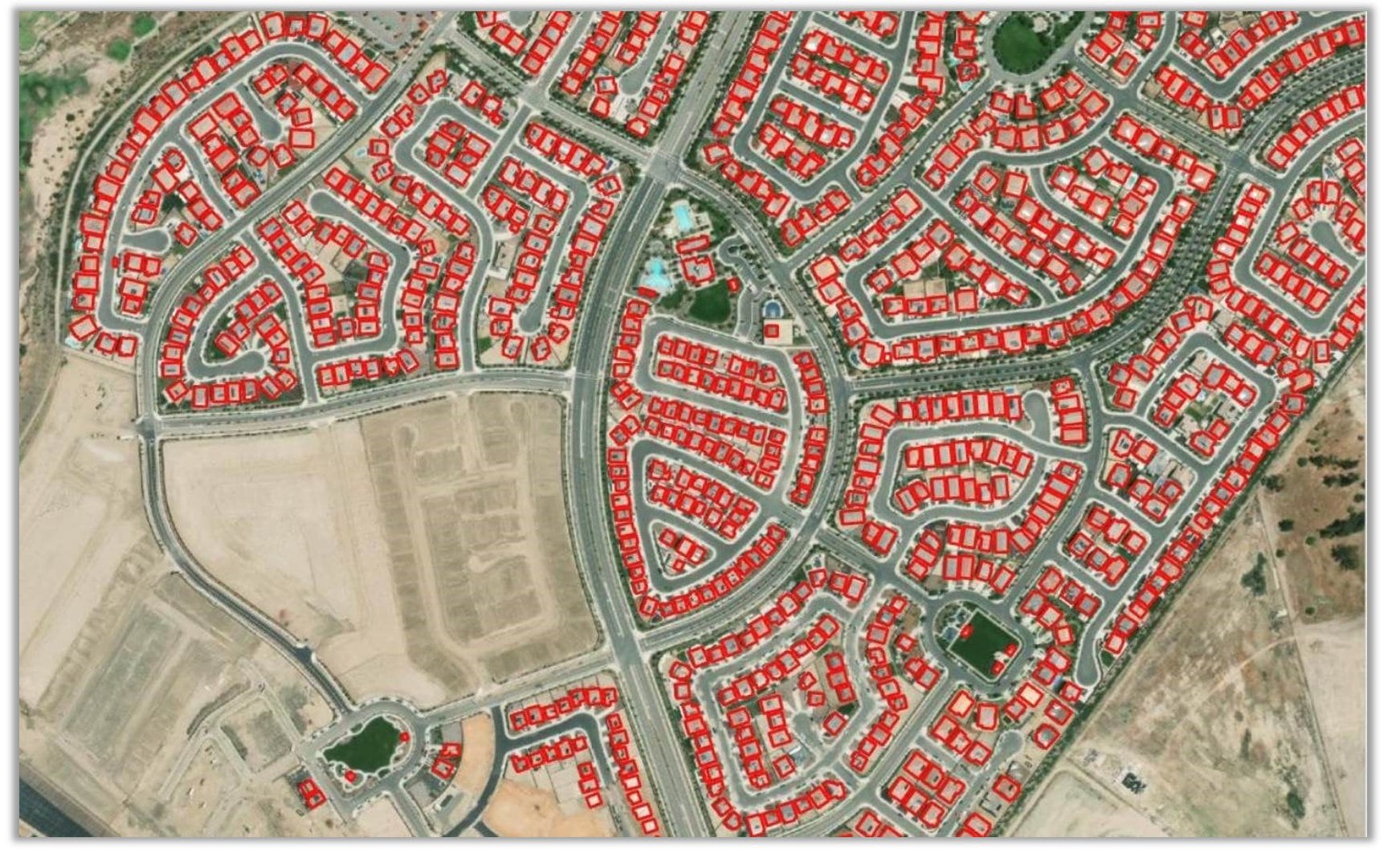

These newly released models are a game changer! They have been pre-trained by Esri on huge volumes of data and can be readily used (no training required!) to automate the tedious task of digitizing and extracting geographical features from satellite imagery and point cloud datasets. They bring the power of AI and deep learning to the Esri user community. What’s more, these deep learning models are accessible for anyone with an ArcGIS Online subscription at no additional cost.
Using the models
Using these models is simple. You can use geoprocessing tools (such as the Detect Objects Using Deep Learning tool) in ArcGIS Pro with the imagery models. Point the tool to the imagery and the downloaded model, and that’s about it – deep learning has never been this easy! A GPU, though not necessary, can help speed things up. With ArcGIS Enterprise, you can scale up the inferencing using Image Server.
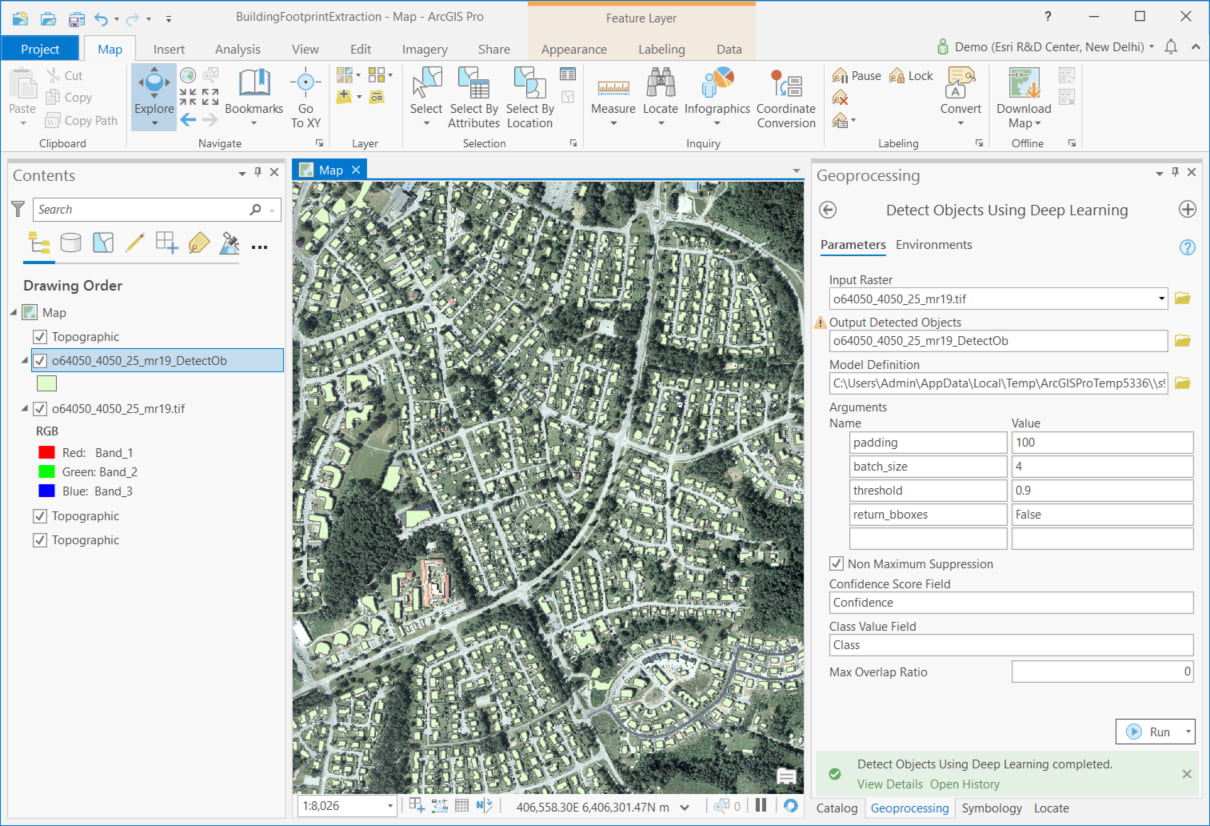
Coming soon, you’ll be able to consume the model directly in ArcGIS Online Imagery and run it against your own uploaded imagery—all without an ArcGIS Enterprise deployment. The 3D Basemaps solution is also being enhanced to use the tree point classification model and create realistic 3D tree models from raw point clouds.
How can you benefit from these deep learning models?
It probably goes without saying that manually extracting features from imagery—like digitizing footprints or generating land cover maps—is time-consuming. Deep learning automates the process and significantly minimizes the manual interaction needed to create these products. However, training your own deep learning model can be complicated – it needs a lot of data, extensive computing resources, and knowledge of how deep learning works.
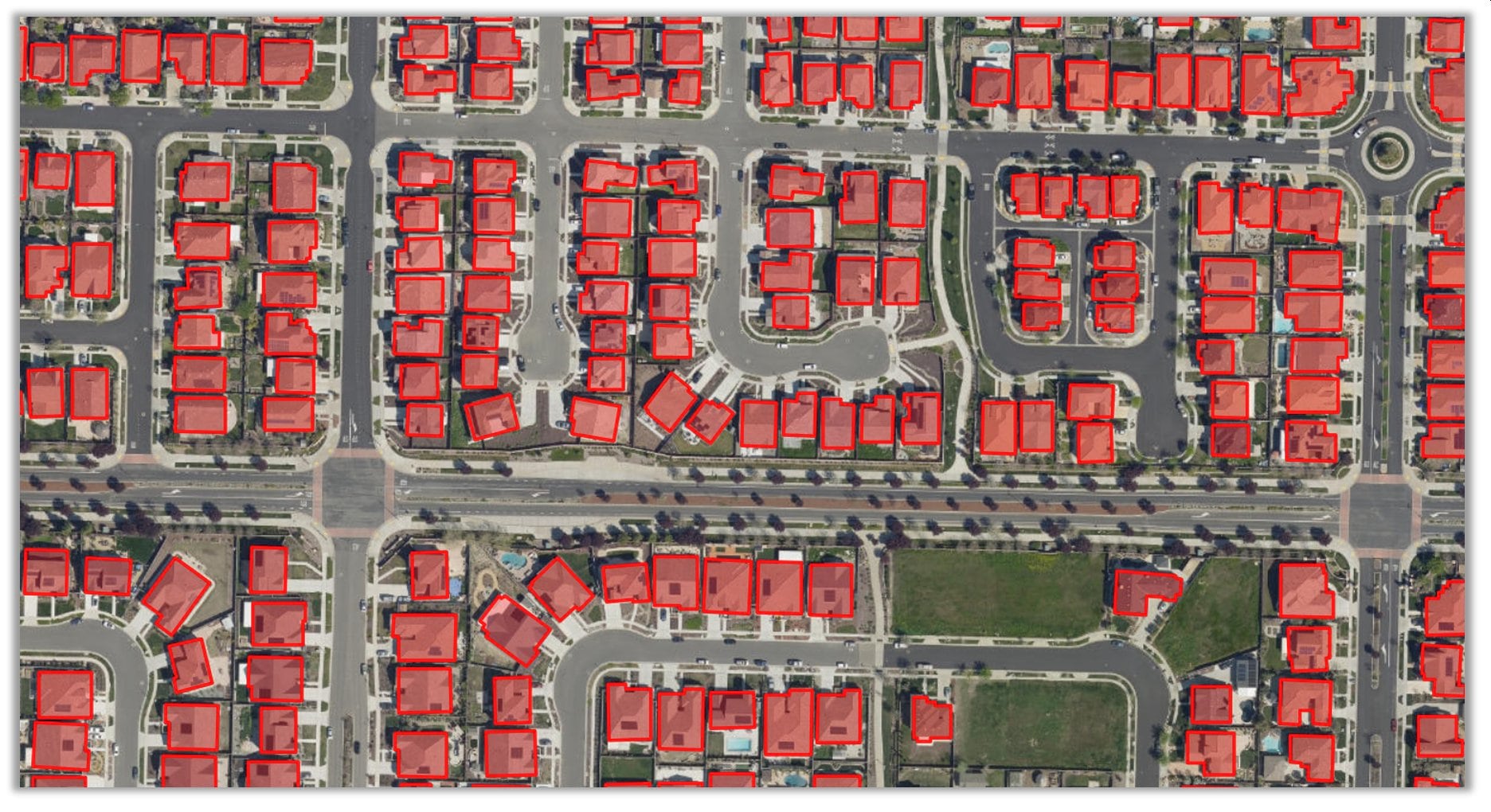

With ready-to-use models, you no longer have to invest time and energy into manually extracting features or training your own deep learning model. These models have been trained on data from a variety of geographies and work well across them. As new imagery comes in, you can readily extract features at the click of a button, and produce layers of GIS datasets for mapping, visualization and analysis.
Get to know the first three models we released
Three deep learning models are now available in ArcGIS Online. (Watch for more models in the future!). These models are available as deep learning packages (DLPKs) that can be used with ArcGIS Pro, Image Server and ArcGIS API for Python.
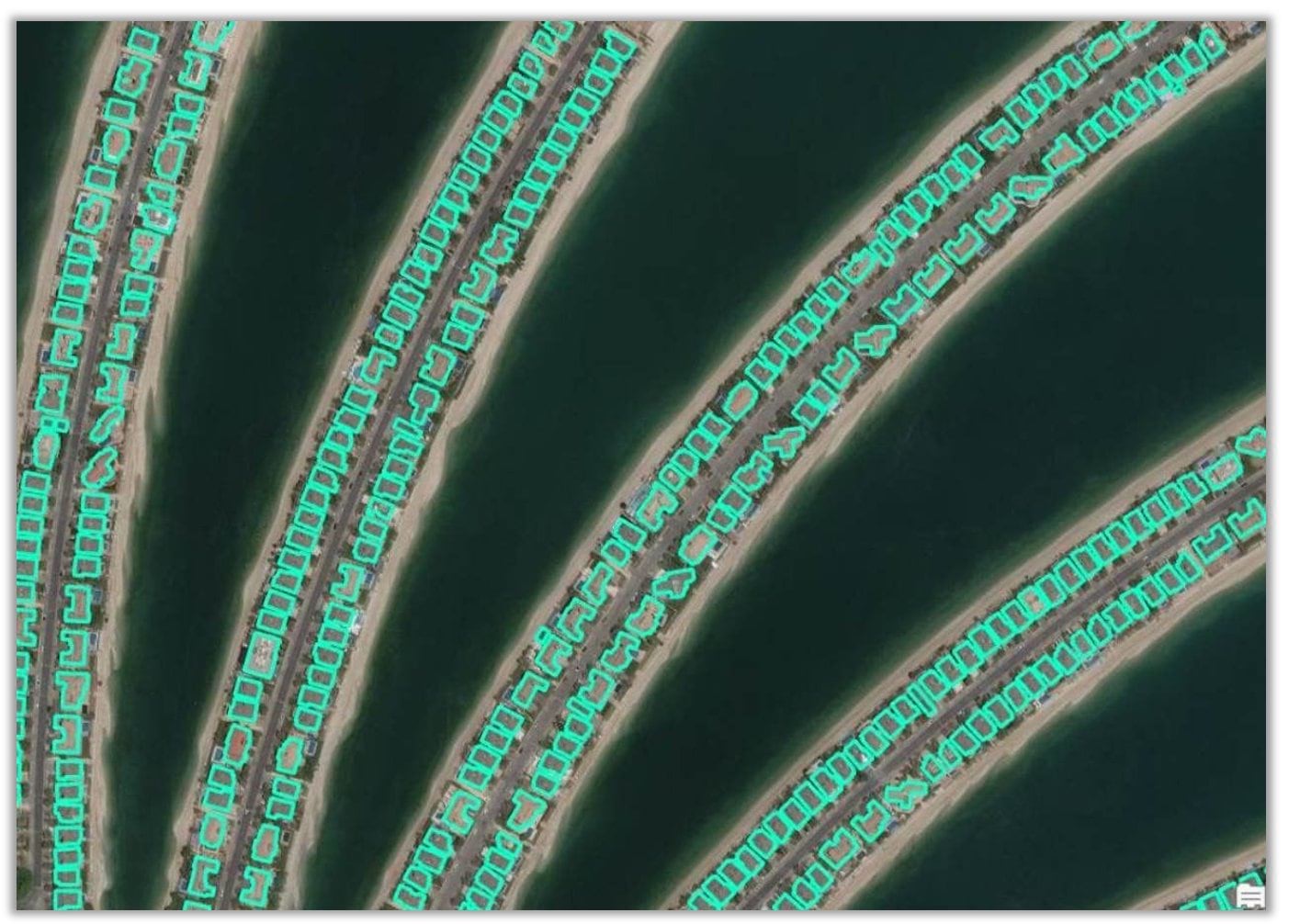
1. Building Footprint Extraction model is used to extract building footprints from high resolution satellite imagery. While its designed for the contiguous United States, it performs fairly well in other parts of the globe.

Here’s a story map presenting some of the results. Building footprint layers are useful for creating basemaps and in analysis workflows for urban planning and development, insurance, taxation, change detection, and infrastructure planning.
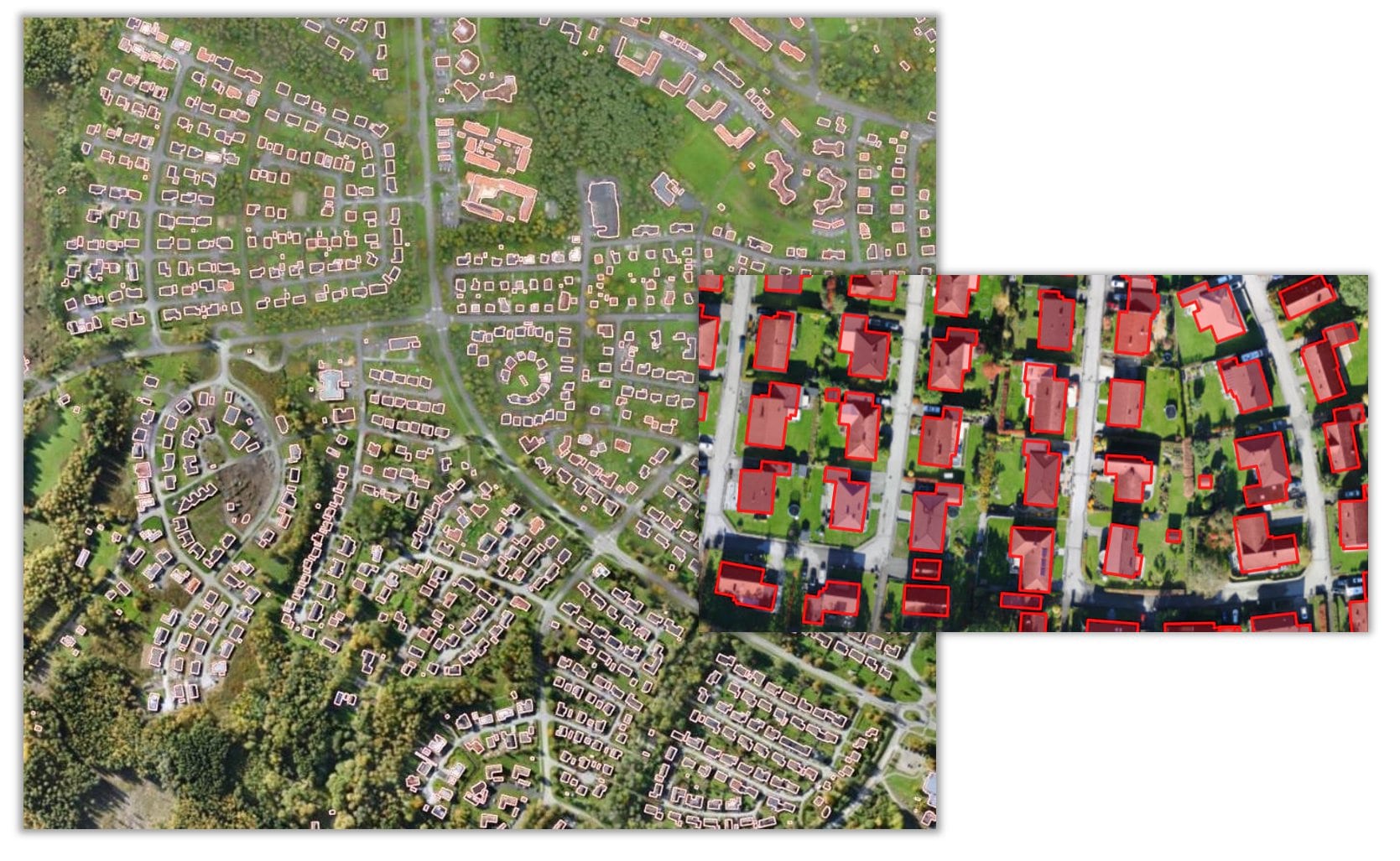
2. Landcover Classification model is used to create a land cover product using Landsat 8 imagery. The classified land cover will have the same classes as the National Land Cover Database. The resulting land cover maps are useful for urban planning, resource management, change detection and agriculture.
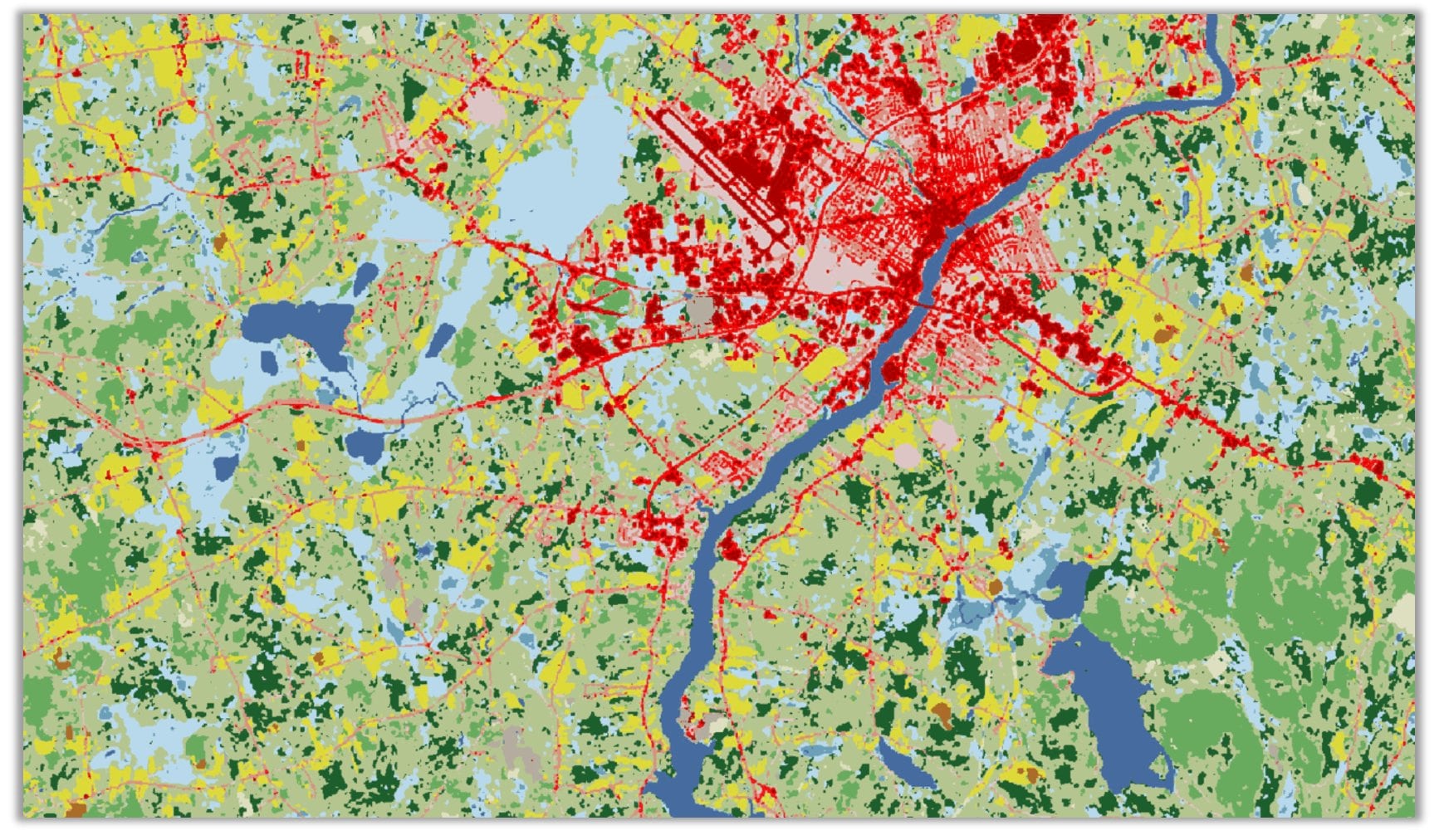
This generic model is has been trained on the National Land Cover Database (NLCD) 2016 with the same Landsat 8 scenes that were used to produce the database. Land cover classification is a complex exercise and is hard to capture using traditional means. Deep learning models have a high capacity to learn these complex semantics and give superior results.
3. Tree Point Classification model can be used to classify points representing trees in point cloud datasets.
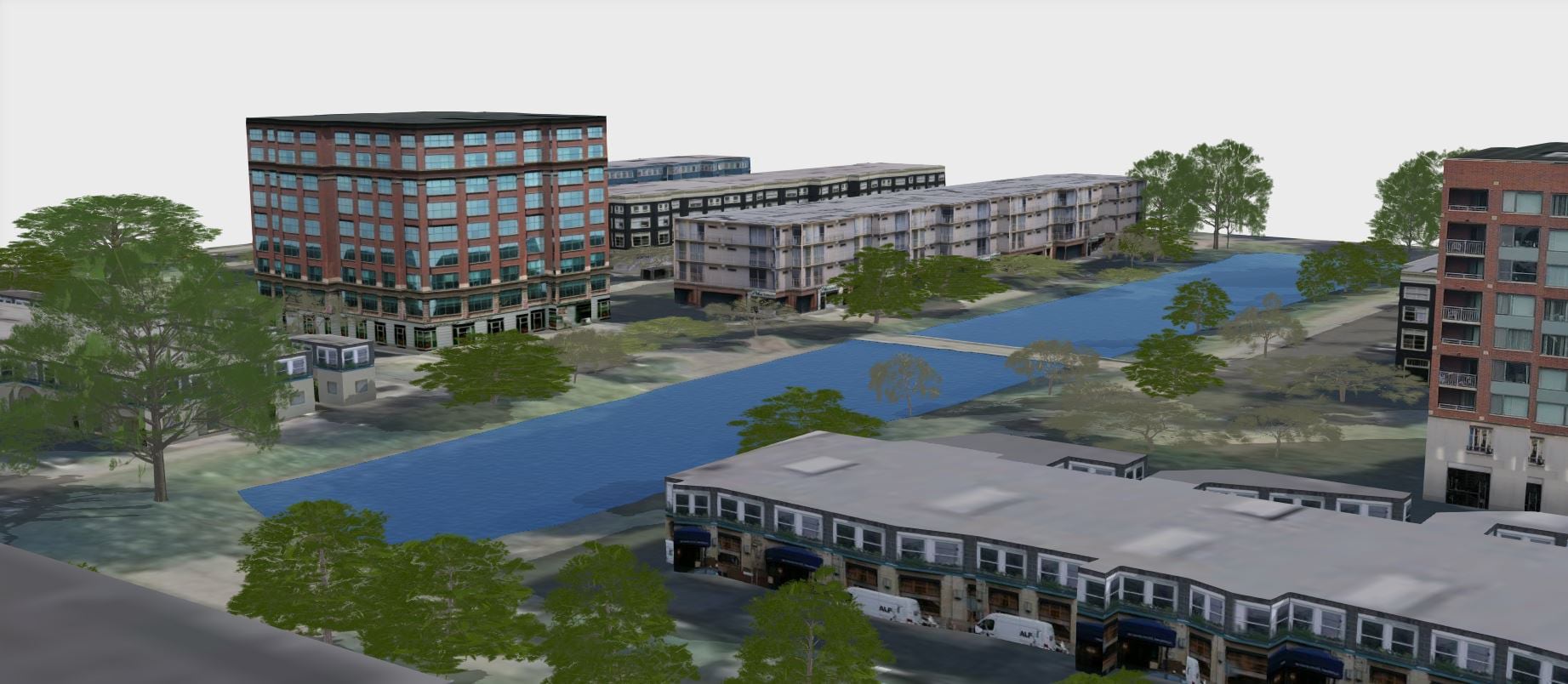

Classifying tree points is useful for creating high quality 3D basemaps, urban planning and forestry workflows.
Next steps
Try out the deep learning models in ArcGIS Living Atlas for yourself. Read more detailed instructions for using the deep learning models in ArcGIS. Have questions? Let us know on GeoNet how they are working for you, and which other feature extraction tasks you’d like AI to do for you!
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
Analysis
10 -
ArcGIS Drone2Map
3 -
ArcGIS Excalibur
1 -
ArcGIS Image Analyst
1 -
ArcGIS Image for ArcGIS Online
1 -
ArcGIS Pro
1 -
Change detection
1 -
Deep learning
4 -
Elevation and lidar
8 -
Image classification
1 -
Image management
2 -
Image Mapping
8 -
Image Services
3 -
Mosaic datasets
4 -
Motion imagery
10 -
Multidimensional
2 -
Oriented Imagery
2 -
Raster functions
4 -
Site Scan for ArcGIS
1 -
Visualization
9
- « Previous
- Next »