- Home
- :
- All Communities
- :
- Products
- :
- ArcGIS AppStudio
- :
- ArcGIS AppStudio Blog
- :
- Introducing the GNSS Info sample app
Introducing the GNSS Info sample app
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
The new GNSS Info sample, included in AppStudio 3.0 Desktop Edition, brings together the components in Qt and the AppStudio AppFramework that you can use to build an app that interacts with GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receivers.
Common features of this type of apps are:
- The requirement to browse and connect to a receiver
- Display a location on a map along with metadata about that location
- Presentation of available satellite information
- Presentation of key quality parameters that may indicate the usefulness of the data received
- Display a raw feed of the data coming from the receiver for troubleshooting purposes
Each of these features are shown in this app on separate tabs. You may choose to use one or more of these tabs in your own app, or use this app as it is, to test out your own GNSS receivers with your hardware.
What type of receivers can be used?
This app will connect to, and display location information from, GNSS receivers that output NMEA sentences. For examples of recievers that we have tested with see GPS receiver support—AppStudio for ArcGIS | ArcGIS .
Qt and the AppFramework can also read and write data to other bluetooth devices using the same components used in this app. For example, you can connect to a bluetooth printer using the same device discovery component and send data from your app to the printer for immediate printing.
For more information on the key components in this sample refer to:
- DeviceDiscoveryAgent - http://doc.arcgis.com/en/appstudio/api/reference/framework/qml-arcgis-appframework-devices-devicedis...
- PositionSource - http://doc.arcgis.com/en/appstudio/api/reference/framework/qml-arcgis-appframework-positioning-posit...
- SatelliteInfoSource – http://doc.arcgis.com/en/appstudio/api/reference/framework/qml-arcgis-appframework-positioning-satel...
- NmeaSource - http://doc.arcgis.com/en/appstudio/api/reference/framework/qml-arcgis-appframework-devices-nmeasourc...
Receiver detection
This app can detect receivers that are connected to your device using:
- Bluetooth pairing – to connect to a receiver in your app you must first pair it with your device. Note that some receivers have a limit to the number of devices they can be paired to at anyone time. For example, the Eos Arrow can only pair to one device at a time, while Bad Elf devices can pair with up to 2 devices at a time. For information on pairing your reciever see Use a high-accuracy GPS receiver—AppStudio for ArcGIS | ArcGIS .
- USB/COM connection – A GPS receiver that plugs into a computer via USB is displayed in the app as a COM port. To confirm which COM port your device is represented by, look at the list of devices connected to your computer. For example, on Windows go to Device Manager > Ports (COM & LPT).
- TCP/UDP network connection – A TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connection is bidirectional and has limited error handling. On the other hand, UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is one way only and has no error handling. Creation of a UDP connection requires the hostname and port of the destination machine (where you are running the app), while creation of a TCP connection requires the hostname and port of the machine providing the GNSS information to the destination machine.
On the device tab, press to select a device. Next time you launch the GNSS Info app, it will attempt to automatically connect to the last device used. You can always return to the device tab and change which device you connect to.
Location display
The location tab shows the current location on a map. If your device has network connectivity, an online basemap is used. A limited offline basemap is also available in the sample.
Key metadata about the current location is displayed. The app also allows the user to change the units in which latitude and longitude are displayed.
Use the location tab to confirm that the location reported from your hardware is the expected location.

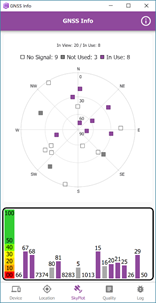
Satellite sky plot
The skyplot tab shows both a skyplot and a table view of the satellites reported by the receiver. Be aware that some receivers have a physical display that may sometimes display different values to this page. Other receivers have their own companion app that also may show different results. These differences are mostly likely attributed to manufacturer specific parameters and the way each manufacturer presents data from the receiver.
The GNSS Info app displays the number of satellites in view, and the amount in use to calculate your location. There can also be satellites in view (or in use) that have no signal. This is usually a temporary response and should not affect the quality of a location displayed in an app.
Use the skyplot tab to ensure you have positioned yourself or your hardware in the best location to capture a suitable position value.
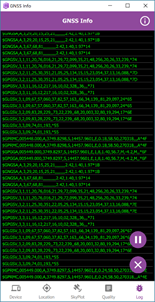
Quality tab
The quality tab lists common meta data available from a GNSS receiver. These are values you may choose to capture during data collection as attributes of your feature. Alternatively, you may use these to indicate the quality of the position to the user. For example, you might warn the user that accuracy values are greater than a prescribed threshold and disallow them to capture data.

Log tab
The log tab shows a stream of the sentences that are emitted from the receiver. Different receivers output different sent
ences. The presence or absence alone of sentences is useful for troubleshooting a receiver connection issue. The inspe
ction of the presence or absence of individual sentences can also aid diagnosis of unexpected parameter results. For example, latitude, longitude and altitude errors are only calculated when the GST sentence is present. Not all receivers
output the GST sentence. If the GST sentence is not available, then ‘No Data’ is reported on the quality tab for latitude, longitude and altitude error.
Use the pause button on this tab to study the latest sentences. Use the delete button to clear the screen to make it easier to read new sentences.
Switching between the tabs of this app will display to you the continuous stream of data reported from the connected GNSS receiver in several ways: as text, on a map, as a graphical representation, and in its rawest form. You can choose which of these best suits your own app, or use this app to evaluate what information is available to you from your own receiver.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
